Routing with Open vSwitch in Routed Mode (with Pre-NAT Hop)
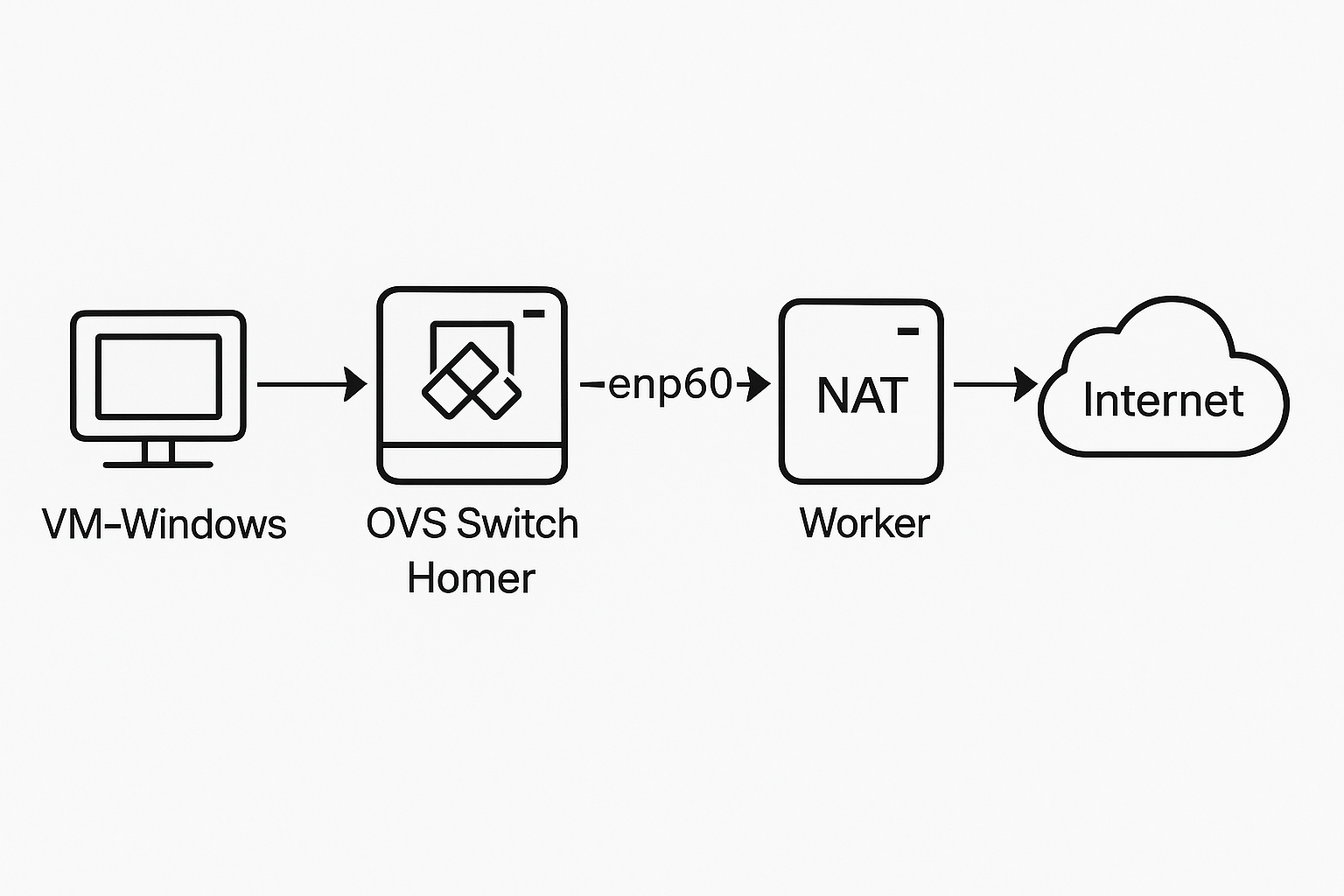
Routing with Open vSwitch in Routed Mode (with Pre-NAT Hop)
This guide outlines a practical and effective way to route traffic through an Open vSwitch (OVS) setup in a routed network topology, where virtual machines (VMs) on one subnet are forwarded through an intermediate router (host) to a NAT gateway.
🔧 Scenario
- VM Subnet:
172.20.1.0/24(routed viahomer) - LAN Subnet:
172.16.0.0/24(onworker, which performs NAT) - Public interface:
enp6s0onworker(dynamic IP, NAT target) - Goal: Allow VMs to reach the internet via an OVS bridge and NAT on another machine
🏗️ Network Architecture
[Windows VM] ──> [OVS bridge: vmnetwork1] ──> [homer] ──> [OVS bridge: office1] ──> [worker: NAT] ──> Internet
🛠️ Key Components
- Open vSwitch bridges:
vmnetwork1andoffice1 - Interfaces:
vmnet1(added automatically by virt-manager)mgmt1(homer LAN-side port)ens6,enp6s0onworker(LAN + WAN)
1. Configure OVS Bridges
On homer:
ovs-vsctl add-br vmnetwork1
# vmnet1 is automatically added by virt-manager; do not add manually
ovs-vsctl add-br office1
ovs-vsctl add-port office1 enp6s0
ovs-vsctl add-port office1 mgmt1 -- set interface mgmt1 type=internal
admin@homer:/home/admin# ovs-vsctl show
da8fa1c2-936b-4e3b-b198-a76353b8dd34
Bridge office1
Port mgmt1
Interface mgmt1
type: internal
Port office1
Interface office1
type: internal
Port enp6s0
Interface enp6s0
Bridge vmnetwork1
Port vmnet1
Interface vmnet1
type: internal
Port vmnetwork1
Interface vmnetwork1
type: internal
ovs_version: "3.3.0"
2. Set IP Addresses on homer
ip addr add 172.20.1.1/24 dev mgmt1
ip addr add 172.16.0.5/24 dev mgmt1
ip link set mgmt1 up
3. Enable Routing on homer
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
And persist in /etc/sysctl.d/99-forward.conf:
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
4. nftables on homer
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority 0;
policy drop;
ip saddr 172.20.1.0/24 ip daddr 172.16.0.0/24 accept
ip saddr 172.16.0.0/24 ip daddr 172.20.1.0/24 accept
ip saddr 172.20.1.0/24 oif mgmt1 accept
ct state established,related accept
}
5. Routing/NAT on worker
Enable forwarding:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
nftables Full nftables config on worker
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
flush ruleset
# Filter Table
table inet filter {
chain input {
type filter hook input priority 0;
policy drop;
iif lo accept
ct state invalid drop
tcp flags & (fin|syn|rst|psh|ack|urg) == (fin|syn|rst|psh|ack|urg) drop
tcp flags == 0x00 drop
ip frag-off & 0x1fff != 0 drop
ct state established,related accept
iif ens6 ip protocol icmp accept
iif enp6s0 ip protocol icmp accept
iif ens6 accept
iif enp6s0 ip daddr != { 172.16.0.0/24, 172.20.1.0/24, 172.21.1.0/24 } tcp dport { 80, 443 } ct state new limit rate 25/second accept
ip saddr { 172.16.0.0/24, 172.20.1.0/24, 172.21.1.0/24 } oif enp6s0 accept
}
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority 0;
policy drop;
ct state established,related accept
iif ens6 oif enp6s0 accept
iif enp6s0 oif ens6 ct state established,related accept
ip saddr 172.20.1.0/24 oif enp6s0 log prefix "VM→WAN: " accept
ip saddr 172.16.0.0/24 oif enp6s0 log prefix "LAN→WAN: " accept
ip saddr { 172.16.0.0/24, 172.20.1.0/24, 172.21.1.0/24 } oif enp6s0 accept
}
chain output {
type filter hook output priority 0;
policy accept;
}
}
# NAT Table
table ip nat {
chain prerouting {
type nat hook prerouting priority -100;
ip saddr { 172.16.0.0/24, 172.20.1.0/24, 172.21.1.0/24 } ip daddr 80.0.130.164 dnat to 172.16.0.1
ip saddr { 172.16.0.0/24, 172.20.1.0/24, 172.21.1.0/24 } log prefix "PREROUTING-NAT: " accept
}
chain postrouting {
type nat hook postrouting priority 100;
ip saddr { 172.16.0.0/24, 172.20.1.0/24, 172.21.1.0/24 } oif enp6s0 masquerade
ip saddr { 172.16.0.0/24, 172.20.1.0/24, 172.21.1.0/24 } oif enp6s0 log prefix "POSTROUTING-NAT: " accept
}
}
nftables NAT:
chain postrouting {
type nat hook postrouting priority 100;
ip saddr { 172.16.0.0/24, 172.20.1.0/24 } oif enp6s0 masquerade
}
nftables Full nftables config on worker
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
flush ruleset
table inet filter {
chain input {
type filter hook input priority 0;
policy drop;
# Allow established/related
ct state established,related accept
# Allow loopback
iif lo accept
# Allow SSH (adjust as needed)
tcp dport 22 accept
# Allow ICMP
ip protocol icmp accept
ip6 nexthdr icmpv6 accept
}
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority 0;
policy drop;
# Allow VM ↔ LAN routing
ip saddr 172.20.1.0/24 ip daddr 172.16.0.0/24 accept
ip saddr 172.16.0.0/24 ip daddr 172.20.1.0/24 accept
# Allow VM subnet to route to WAN via mgmt1
ip saddr 172.20.1.0/24 oif mgmt1 accept
ip saddr 172.20.1.0/24 oif mgmt1 log prefix "HOMER-DROP: " drop
# Allow established/related flows
ct state established,related accept
}
chain output {
type filter hook output priority 0;
policy accept;
}
}
6. Configure Virt-Manager and XML Network
To integrate this network with virt-manager, define a routed virtual network using the following XML example:
<network connections="1">
<name>vmnetwork1</name>
<uuid>ec8d7631-18b8-454b-b506-73ac2ff66202</uuid>
<forward dev="vmnetwork1" mode="route">
<interface dev="vmnetwork1"/>
</forward>
<bridge name="virbr0" stp="on" delay="0"/>
<mac address="52:54:00:87:f5:0e"/>
<domain name="vmnetwork1"/>
<ip address="172.20.1.1" netmask="255.255.255.0">
<dhcp>
<range start="172.20.1.128" end="172.20.1.254"/>
</dhcp>
</ip>
</network>
Use virsh net-define and virsh net-start to enable it. Avoid naming conflicts with default networks like virbr0.
7. Configure VM (Windows)
Set default gateway to 172.20.1.1 (homer).
Add static route for LAN access if needed: (in validation we ended up not needing it)
route -p add 172.16.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 172.20.1.1
✅ Testing
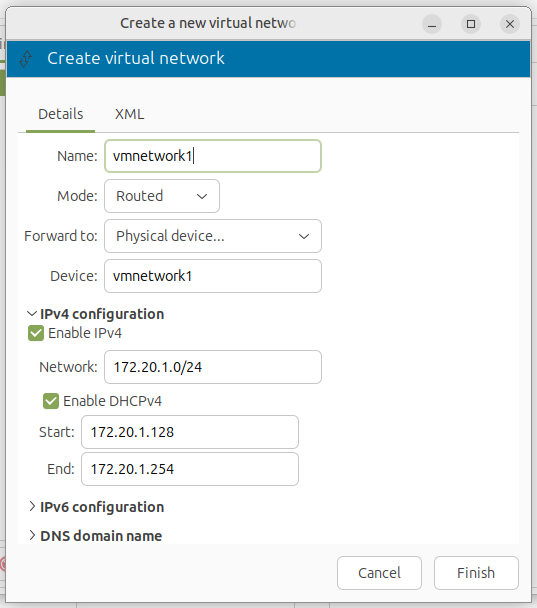
Setup Virt-Manager to use the new network
Step 1
Step 2 - review
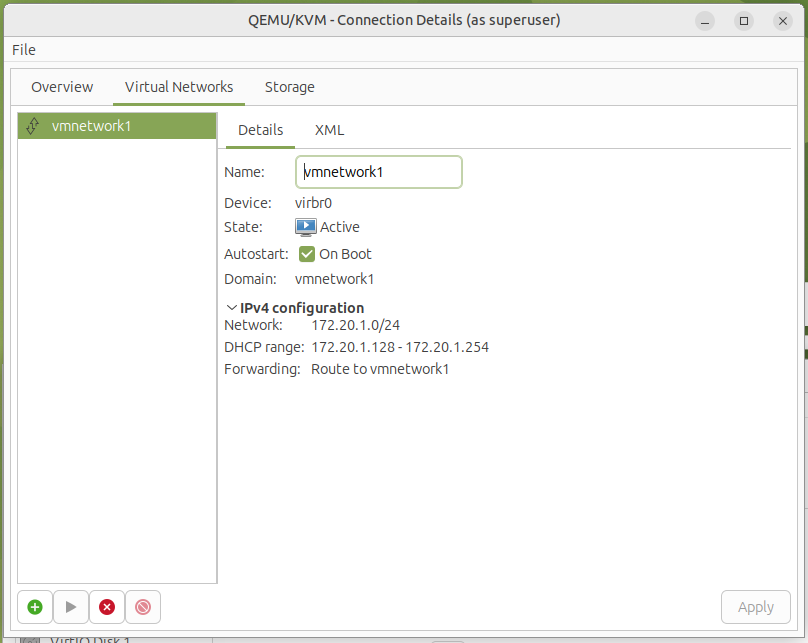
Or manually create a network
<network connections="1">
<name>VM Network1 Name</name>
<forward dev="vmnetwork1" mode="route">
<interface dev="vmnetwork1"/>
</forward>
<bridge name="virbr0" stp="on" delay="0"/>
<domain name="vmnetwork1"/>
<ip address="172.20.1.1" netmask="255.255.255.0">
<dhcp>
<range start="172.20.1.128" end="172.20.1.254"/>
</dhcp>
</ip>
</network>
Use the following commands to define and start the network:
virsh net-define /path/to/vmnetwork1.xml
virsh net-autostart vmnetwork1
virsh net-start vmnetwork1This will register the network with libvirt, enable autostart, and bring it online for use in virt-manager. Avoid naming conflicts with default networks like virbr0.
✅ Validation
ping 172.16.0.1(worker LAN IP) ✅ping 8.8.8.8ortracertfrom VM ✅tcpdumpandjournalctlused to trace NAT and route drops
C:\Users\akadata>tracert google.com
Tracing route to google.com [142.250.187.206]
over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 <1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 172.20.1.1
2 <1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 172.16.0.1
3 * * * Request timed out.
4 8 ms 9 ms 10 ms 80.255.193.212
5 * * * Request timed out.
6 17 ms 20 ms 20 ms eislou2-ic-3-ae0-0.network.virginmedia.net [94.174.238.226]
7 19 ms 17 ms 17 ms 72.14.221.42
8 20 ms 19 ms 18 ms 192.178.97.179
9 20 ms 19 ms 21 ms 142.251.54.33
10 24 ms 22 ms 19 ms lhr25s33-in-f14.1e100.net [142.250.187.206]
Trace complete.🧠 Notes
- This setup keeps VM routing clean and offloads NAT to a robust external host.
- Split DNS and internal
.labdomains can easily follow this foundation. - Logging temporary
log prefixrules innftablesis invaluable during setup.
🔮 Future Enhancements
- Add
vmnetwork0bridge onworkerto segregate VM traffic from the LAN. - Implement split-horizon DNS using
.labfor internal services. - Add
dnsmasqorunboundto serve.labzone only over internal interfaces. - Consider enabling
radvdfor IPv6 delegation to VMs if desired. - Introduce firewall zone tagging and VLAN separation per interface role.
