Tech Scrolls 10:2 — Reveal Your Real Location, Walk in Truth
He leads those who wish to be seen as they are, not as their ISP's shadow, to dwell in the land and be found, not hidden.
(Tech Scrolls 7:1)
Introduction
The world runs on trust and presence. In an age of virtual networks, tunnels, and remote work, a user may wish to show their true (or at least plausible) geographic location to the web, not where the ISP backbone or tunnel endpoint happens to be. This is not for evasion or fraud — but for dignity and accuracy. Whether it is dating, delivery, business, or simply being seen as present, there is value in showing who you are and where you live.
This article explores how to override browser geolocation in Firefox (and, where possible, other browsers) on Linux, Mac, and Windows. We'll explain how to:
- Serve geolocation from a local GPS (or a fixed JSON file) instead of Google
- Fuzz your exact location to avoid oversharing
- Use Python scripts to power your browser’s location service
- Never send your movements to third parties
Principle
- The aim is trust, not deception: show your true city or town, not a backbone in London, Amsterdam, or a tunnel endpoint.
- Reveal what you choose, not what the browser guesses or Google says.
- Works for dating, delivery, weather, job searches, and more.
How Browser Geolocation Works (Firefox Example)
Browsers typically call a web service — often Google — to determine your position. Firefox allows overriding this by changing the geo.provider.network.url (and related keys) in about:config.
How to Override Geolocation in Firefox
Step 1: Write or Choose a Location Provider
Option A: Local GPS (Python, gpsd, Real Accuracy)
- Use
gpsdwith a USB/Bluetooth/serial GPS. - Serve live JSON via a Python script (see below) on
http://localhost:8080/geo.
Option B: Fixed or Fuzzed JSON File (Python, Static City/Town)
- Serve a single city/town/region — no need for Google, no tracking.
Option C: WiFi Scan or Mobile Tethering (Advanced, Optional)
- Advanced: Use WiFi scan data, with debug tools on mobile, to enhance accuracy (not required for basic town/city location).
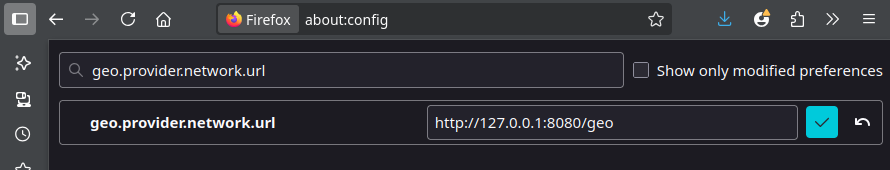
Step 2: Set Firefox to Use Your Location Provider
- Open
about:configin Firefox. - Search for
geo.provider.network.url. - Set it to:
localhostor127.0.0.1there's no place like homehttp://localhost:8080/geo(for live GPS or Python script)- Or to a local static file served via Python/simple HTTP server.
- Optional: Set
geo.provider.network.timeoutto 2 or 3 (seconds). - Optional: Set
geo.provider.network.logging.enabledto true for debugging.
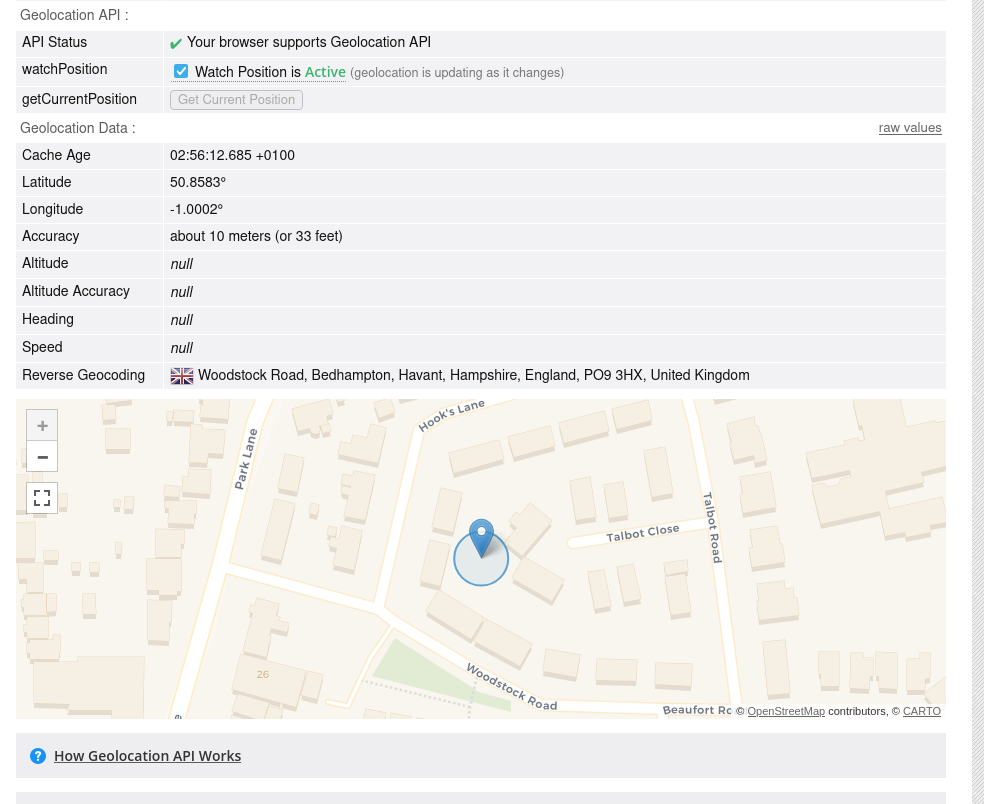
Step 3: Test Geolocation
- Visit https://browserleaks.com/geo or any map/dating/delivery site.
- Confirm you appear in your true or intended location or at least where you intend to be found.
- Location below is close to where you may live, not the exact address however it may be the same town, not a million miles away from the truth.
Example Python Code — Live GPS
Place this at /usr/local/bin/gps-locationd.py (Linux/Mac, but also possible under WSL or Windows with GPSD):
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from http.server import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, HTTPServer
from gps import gps, WATCH_ENABLE, WATCH_NEWSTYLE
import json
import time
DEFAULT_LAT = 50.8583
DEFAULT_LON = -1.0002
ACCURACY = 10
session = gps(mode=WATCH_ENABLE | WATCH_NEWSTYLE)
class LocationHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def get_position(self):
try:
# Attempt several times in case of temporary fix loss
for _ in range(5):
report = session.next()
if report['class'] == 'TPV':
lat = getattr(report, 'lat', None)
lon = getattr(report, 'lon', None)
mode = getattr(report, 'mode', 0)
if mode >= 2 and lat is not None and lon is not None:
return float(lat), float(lon)
time.sleep(0.2)
except Exception:
pass
return DEFAULT_LAT, DEFAULT_LON
def do_POST(self):
if self.path == "/geo":
lat, lon = self.get_position()
response = {
"location": {
"lat": lat,
"lng": lon
},
"accuracy": ACCURACY
}
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header('Content-Type', 'application/json')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(response).encode())
else:
self.send_error(404)
def do_GET(self):
# Optional for testing
lat, lon = self.get_position()
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header('Content-Type', 'application/json')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(json.dumps({
"location": {
"lat": lat,
"lng": lon
},
"accuracy": ACCURACY
}).encode())
def log_message(self, format, *args):
return # silence all logging
def run():
server = HTTPServer(('0.0.0.0', 8080), LocationHandler)
server.serve_forever()
if __name__ == "__main__":
run()Systemd unit available for auto-start on Linux.
/etc/systemd/system/gps-locationd.service
[Unit]
Description=GPS Location HTTP server for Firefox
After=network.target gpsd.service
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/gps-locationd.py
Restart=on-failure
User=nobody
Group=nogroup
ProtectSystem=full
ProtectHome=true
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetExample Python Code — Fuzzed/Privacy-Friendly Location
Place at /usr/local/bin/gpsd-fuzz.py and run as service or from CLI:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import gps
import socketserver
import random
import json
import time
# Fuzz radius in degrees (~0.001 = ~100m)
RADIUS = 0.0025
def fuzz(val, radius=RADIUS):
return val + random.uniform(-radius, radius)
session = gps.gps(mode=gps.WATCH_ENABLE)
class GPSServer(socketserver.BaseRequestHandler):
def handle(self):
while True:
report = session.next()
if report['class'] == 'TPV':
if hasattr(report, 'lat') and hasattr(report, 'lon'):
data = {
'class': 'TPV',
'lat': fuzz(report.lat),
'lon': fuzz(report.lon),
'alt': getattr(report, 'alt', 0),
'time': getattr(report, 'time', '')
}
self.request.sendall((json.dumps(data) + '\n').encode())
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
with socketserver.TCPServer(('0.0.0.0', 2948), GPSServer) as server:
server.serve_forever()Serving a Static Location (Simple JSON)
If you have no GPS, create a file (e.g., city.json):
{"location": {"lat": 50.8583, "lng": -1.0002}, "accuracy": 150}
And serve with Python:
python3 -m http.server 8080
# or use a tiny Flask server, or anything that serves city.json at /geo
Then set geo.provider.network.url to http://localhost:8080/city.json.
Why Not Just Use Google’s Default? (The Problem)
- ISPs, tunnels, mobile networks often report you far from where you are.
- Dating sites (including Tinder) and delivery sites often see the wrong city, or even the wrong country. With Tinder, for example, once you've signed up from a desktop or laptop, your location is forever tied to wherever your ISP exits to the internet, unless you pay for the 'Passport' feature. This simple change lets you finally connect with the local audience you truly want, without faking, hiding, or paying for extras, just revealing your genuine presence in your chosen town or city.
- Revealing where you are is about trust and truth, not hiding.
Advanced: WiFi & Mobile Data
- With mobile debug or WiFi scan, your device can report access points to improve accuracy (advanced, not needed for most users).
- Use GPS when you want true street-level precision.
- You may choose to “fuzz” by randomising coordinates within a set radius.
Windows/Mac: Tips
- Use WSL for Python on Windows, or serve via another box and set the local URL.
- On Mac, use Homebrew for Python and GPSD.
Final Thoughts: Dignity, Not Deceit
This approach gives you (and your browser) the ability to show the world where you truly are, with the level of precision you choose. It is not for fraud or hiding, but for restoring trust in a digital age where ISPs and backbones obscure our reality. Walk in truth; enable your real presence online.
